

Chemical Shifts
The NMR spectra is displayed as a plot of the applied radio frequency versus the absorption. The applied frequency increases from left to right, thus the left side of the plot is the low field, downfield or deshielded side and the right side of the plot is the high field, upfield or shielded side (see the figure below). The concept of shielding will be explained shortly.
- Delta™ is the software that empowers our ECZ series NMR systems. Never has a software package with such powerful control and processing been so easy to use. Multi-dimensional visualization (up to 4D) and processing (up to 8D) are just part of the standard package.
- Analytical Chemistry Software Solutions. A shared interface with automation abilities that allows users to optimize their learning curve and workflows by combining different technique data on the same application. Processing & analyzing LC/GC/MS data made simple. NMR processing, analysis, simulation and reporting.

One-of-a-kind software to help you get answers from analytical data no matter the analytical technique or instrument vendor. Process, interpret, analyze, and review NMR, LC/MS, IR, and other analytical data, in one interface. ACD/Spectrus Processor provides support for all your major instrument vendor data formats (view supported data formats. Delta NMR Software Installing Delta: Copy the appropriate Delta install file (either PC or Mac) from the department NMR website or one of the CDs in the library to your desktop. Double click on the file to begin the installation. Follow the directions during the install. During the install choose minimal for the Installation Set.
The position on the plot at which the nuclei absorbs is called the chemical shift. Since this has an arbitrary value a standard reference point must be used. The two most common standards are TMS (tetramethylsilane, (Si(CH3)4) which has been assigned a chemical shift of zero, and CDCl3 (deuterochloroform) which has a chemical shift of 7.26 for 1H NMR and 77 for 13C NMR.
The scale is commonly expressed as parts per million (ppm) which is independent of the spectrometer frequency. The scale is the delta (δ) scale.
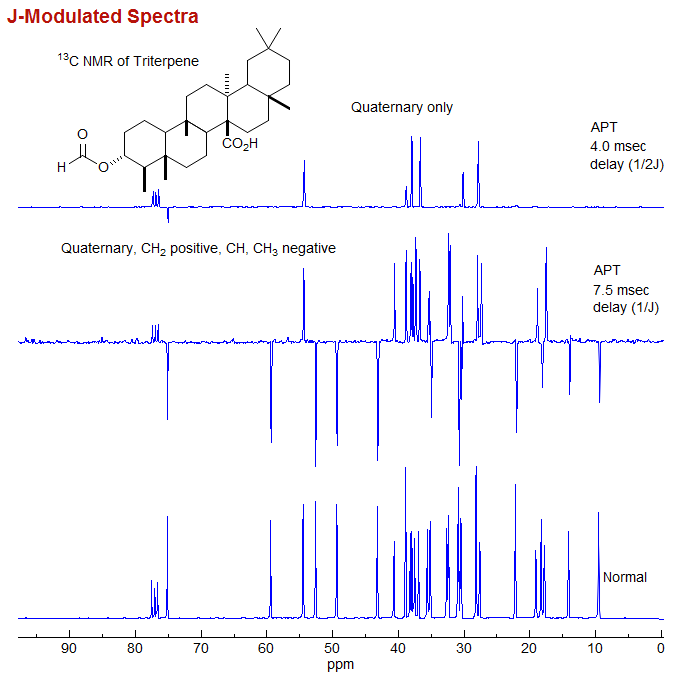
Delta Software For Nmr Spectra Lab
The range at which most NMR absorptions occur is quite narrow. Almost all 1H absorptions occur downfield within 10 ppm of TMS. For 13C NMR almost all absorptions occurs within 220 ppm downfield of the C atom in TMS.
CHEM 350 - Principles of Organic Chemistry I Experiment #2 - Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. 13C NMR Spectra of some Alkanes and Alkenes References: Klein Chapter 16, Mohrig Chapter 21.1-21.3, 22.1-22.3 Pre-Lab Assignments: 1. Prepare a pre-lab plan in your lab notebook that is specific for your group's assigned compound. No need to include data for the compounds that other groups will be examining. Overview: You will join together with another team of three to form a supergroup of six for this lab. (This is for the in-lab procedures only. Each team should continue to keep its own in-lab journal and prepare its own pre-lab plan and report.) Each supergroup will be assigned a compound from among the following list of alkanes and alkenes, hexane, heptane, dodecane, octadecane, cyclohexane, cycloheptane, 2,2-dimethylbutane, 2,3-dimethylbutane, 2-methylpentane, 3-methylpentane, cyclohexene, 1-heptene, and 1-dodecene. Safety Precautions - CDCl3 has harmful fumes. Avoid breathing it and dispense it in a fume hood. Agenda - First, the instructor will present a brief lecture on 13C NMR and the use of the JEOL Delta software for data processing. Then, each supergroup will prepare a sample for NMR analysis and bring it to the NMR lab, where the instructor will demonstrate the operation of the NMR spectrometer and obtain the spectrum. Preparing the Sample. NMR tubes and solvents are very costly so please be very careful with the tubes and do not waste the solvent. Also, be very careful when capping and uncapping your NMR tube. The tubes are fragile and the caps are tight so it is easy to break a tube in the process of capping or uncapping it. Weigh the NMR tube and cap then use a Pasteur pipet or small spatula to add the assigned compound to the NMR tube to a height of approximately 2-3 mm. Cap the tube and reweigh. Add the CDCl3 solvent carefully to a height of 5 cm in the tube. Invert and/or agitate the tube in order to dissolve the assigned compound in the solvent (warning - the caps can leak). Label your tube by writing on the side of the cap with a permanent felt tip marker. Waste Disposal - NMR sample solutions should be drained into the waste solvent container when finished. Be very careful when removing the plastic cap as it is easy to break the top of the tube when doing so. Rinse the tube several times with acetone into the waste solvent container. Store the tube uncapped so the acetone will fully evaporate by the time of its next use. General Instructions for Using Delta 1. Choose 'Process 1D' under the Processors menu and open the file by using the file menu, clicking on the icon, or hitting ctrl<o>. What you see initially is a plot of the NMR signal as a function of time. This is called the 'Free-Induction Decay' or FID. 2. To convert the data to a useable form you need to Fourier Transform it , phase correct it, and set the x-axis units to ppm . 3. To annotate the spectrum with peak chemical shifts use the 'Auto Peak Pick' icon, . 4. Zooming in is accomplished by clicking and dragging on the spectrum. Clicking and dragging in the gray area below the x-axis just zooms in along the x-axis with the y-axis remaining at full scale. Use the keyboard key: 'BackSpace' to revert to the previous (unzoomed) view. 5. Print the spectrum by simply printing on the icon that looks like a printer and selecting the desired printer from the scroll list. Report Class data will be pooled for the purposes of the lab report. NMR spectra for the entire class will be available in the class storage folder. Each file will be clearly named with the name of the compound. Copy these files to your computer and use Delta to process and print them. The instructor will demonstrate the use of this software during the lab and can assist you at the end of the lab period or during office hours as needed. Write the structure of the compound prominently on each spectrum and label all sets of equivalent carbons a, b, c, etc. Now label the peaks in the spectrum a, b, c, etc. to show which carbons in the molecule are represented. Label any extraneous peaks including the TMS peak (if present) and CDCl3 solvent peak. Your results table should summarize the NMR data for all of the compounds. Take care in designing it for optimal conciseness and ease of use. Included should be compound names and structures as well as chemical shifts and assignments for each peak. Use the NIMCR's ISDBS for Organic Compounds to verify your peak assignments and include the literature values for the chemical shifts in the table. Do not include the extraneous peaks (see above paragraph) in the table. Your discussion section should go into each of the following 1. Comment on the accuracy of the chemical shift measurements. Be quantitative. 2. Comment on the general effect of the number of hydrogens attached to an sp3 carbon on its C-13 chemical shift? Use the data to illustrate. Concisely provide a theoretical basis for this effect. 3. Look at the data for the alkenes in comparison to the alkanes. What is the effect of the hybridization of a carbon atom on it chemical shift?Use the data to illustrate. Again, concisley state the theoretical basis for this effect. 4. Can the number of peaks observed in the C-13 spectrum be accurately predicted from the structure? Use the data to illustrate. |